I. Basic introduction of wires and cables
Wire and Cable: it is usually twisted by several or several groups of wires [at least two in each group], similar to ropes. Each group of wires is insulated from each other and often twisted around a center. The whole outside is covered with a highly insulated covering layer. It is mostly used to transmit, distribute electric energy or transmit electrical signals.
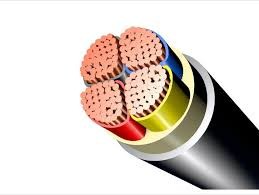
Wires and Cables are mainly composed of the following four parts
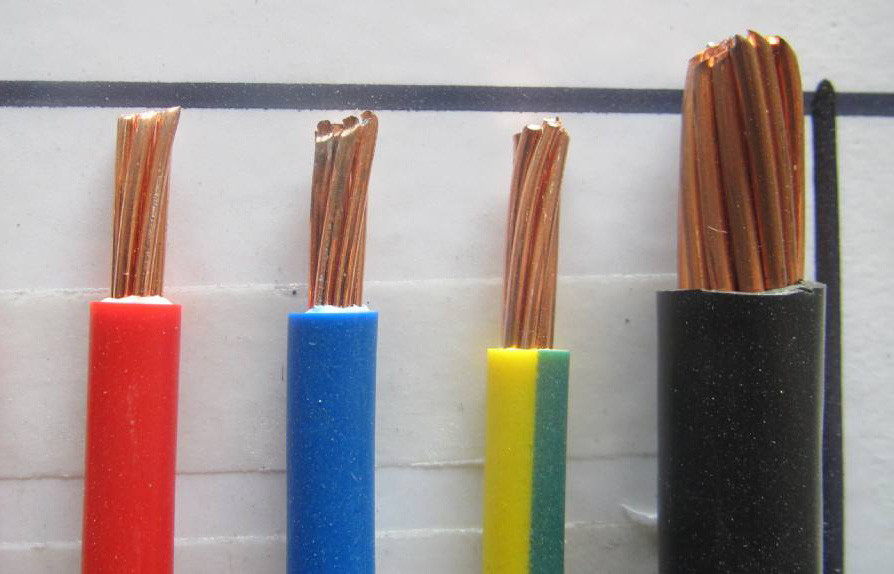
1. Conductive wire core: made of high conductivity material (copper or aluminum). According to the requirements of laying conditions for cable softness, each core may be stranded by a single wire or multiple wires.
2. Insulation layer: insulation material used as cable should have high insulation resistance. Insulation material commonly used in cables include oil-immersed paper, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene, rubber, etc.
3. Sealed jacket: protect the insulated wire core from mechanical, moisture, moisture, chemicals, light, etc. For insulation that is prone to moisture, lead or aluminum is generally used to squeeze sealed jacket.
4. Protective Cover: used to protect sealed jacket from mechanical damage. Galvanized steel strip, steel wire, copper strips wire, copper wire, etc. are generally used as armor to wrap around the sheath (called armored cable), and the armored layer can shield the electric field and prevent the interference of external electromagnetic waves at the same time. In order to avoid the corrosion of steel strips and steel wires by the surrounding medium, they are usually coated with asphalt or wrapped with impregnated jute layer or extruded polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride sleeve.
II. Wire and Cable Specifications
Wire and Cable specifications are the meaning of the representation of the number of cores and cross-sectional dimensions of wires and cables. The complete naming of wires and cables is usually more complicated, so people sometimes use a simple name (usually a category name) combined with model specifications to replace the complete name, for example, "Low Voltage Cable" represents all plastic insulated power cables of 0.6/1kV level. The type spectrum of the cable is relatively perfect. It can be said that as long as the standard model specifications of the wire and cable are written, the specific products can be clearly defined.
III. Application classification of wires and cables
(1) classified by insulation material, such as oil-immersed paper insulated cables, polyvinyl chloride cables, XLPE cables, etc.
(Ii) classified by purpose, divided into power cable, communication cable and control cable, etc. It is applied to power system, information transmission system, mechanical equipment and instrument system respectively.
1. Power system
Wire and cable products used in power system mainly include overhead bare wire, busbar (bus), power cable (plastic cable, oil paper power cable (basically replaced by plastic power cable), rubber-sleeve cable, overhead insulated cable), branch cables (replacing some bus bars), electromagnetic wire, electrical equipment wires and cables for power equipment, etc.
2. Information transmission system
The wires and cables used in information transmission system mainly include local cable, TV cables, electronic cables, radio frequency cables, optical fiber cables, data cables, electromagnetic wire, power communication or other composite cables.
3. Mechanical equipment, instrumentation system
Almost all products except overhead bare wires in this part have applications, but they are mainly power cables, electromagnetic wire cables, data cables, instrument cables, etc.
(3) according to product classification, it is divided into five categories
1. Bare wire and bare conductor products
The main features of this product are: pure conductor metal, no insulation and sheath layer, such as steel core aluminum stranded wire, copper aluminum busbar, electric locomotive wire, etc.; The processing technology is mainly pressure processing, such as smelting, calendering, drawing, stranding/compact stranding, etc.; Products are mainly used in suburbs, rural areas, user main lines, switch cabinets, etc.
2. Power cable
The main features of this kind of products are: Squeezing (winding) insulation layer outside the conductor, such as overhead insulated cable, or several core stranded (corresponding to the phase line, zero line and ground line of the power system), for example, more than two-core overhead insulated cables, or add a sheath layer, such as plastic/rubber cover wire and cable. The main technologies include drawing, stranding, insulation extrusion (wrapping), cable forming, armour, sheath extrusion, etc. Different process combinations of various products have certain differences.
The products are mainly used in the transmission of strong electric energy in the transmission, distribution, transmission, transformation and power supply lines, with large current (tens of to thousands of) and high voltage (220V to 500kV and above).
3. Wires and cables for electrical equipment
The main features of this kind of products are: there are a wide range of variety and specifications, wide range of application coverage, and the operating voltage is more than 1kV. In the face of special occasions, new products are constantly derived, such as fire-resistant cables, Flame Retardant Cables, low smoke halogen-free/low smoke halogen-free cables, termite-proof, mouse-proof cables, oil-resistant/cold-resistant/temperature-resistant/wear-resistant cables, medical/agricultural/mining cables, thin-walled wires, etc.
4. Communication cable and optical fiber
From the simple telephone and telegraph cables in the past to thousands of pairs, coaxial cables, optical cables, data cables, and even combined communication cables. The structure and size of this kind of products are usually small and uniform, and the manufacturing precision is required to be high.
5. Electromagnetic wire (winding wire)
It is mainly used for various motors, instruments and meters, etc.
4. What is the difference between wire and cable?
In fact, there is no strict boundary between "wire" and "cable. Generally, products with small core number, small product diameter and simple structure are called wires, those without insulation are called bare wires, and others are called cables; Those with large conductor cross-sectional area (greater than 6 mm²) are called large wires, smaller (less than or equal to 6 mm²) is called small cord, and insulated electric conductor is also called covered wire. However, with the expansion of the scope of use, many varieties of "cable with Cable" and "cable with Cable". Therefore, there is no need to strictly distinguish. In daily habits, people call household covered wire and power cable for short.
The wire is composed of one or several soft wires, and the outer bread has a light and soft protective layer; The cable is composed of one or several insulated covered wires, the outside is wrapped with a tough outer layer made of metal or rubber. Cables and wires are generally composed of core wire, insulation foreskin and protective sheath.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!